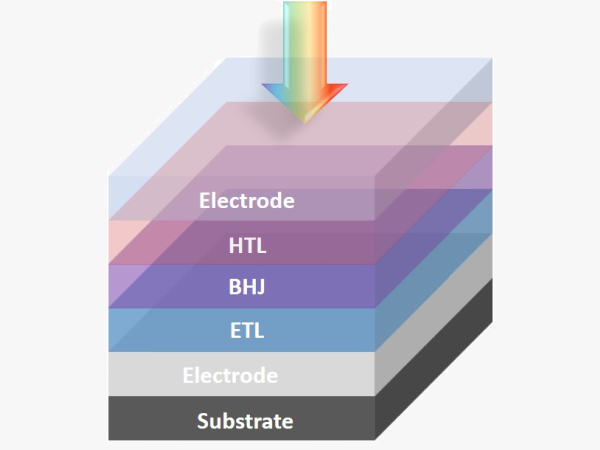
Why Organic Photodetector (OPD) ?
OPD is an emerging optical sensor which using organic semiconductor as photoactive layer, it is promising to replace state of art silicon and inorganic photodetectors with following advantages:
 Tunable Spectral Response
Tunable Spectral ResponseBy adjusting the chemical structure of the organic semiconductor, the spectral sensitivity of OPD can be customized to various wavelengths.
 Short-wavelength and Near Infrared Sensing (SWIR and NIR)
Short-wavelength and Near Infrared Sensing (SWIR and NIR)Mainstream Silicon photodetector has no spectral response beyond 1000 nm while alternative inorganic photodetectors, such as III-V semiconductor are known for the high cost. In this regards, OPD could complement above existing photodetector technologies’ shortcoming by offering tunable spectrum response and cost-effective production, respectively.
 Excellent Absorption Coefficient
Excellent Absorption CoefficientThe absorption coefficient of organic semiconductor is 10~100 times higher than inorganic semiconductors, it keeps the sensitivity of photodetector under sub-micro pixel.
 Enhance Next-generation Image Sensor
Enhance Next-generation Image SensorThanks to readiness of OLED on silicon product, the process compatibility of organic semiconductor on a readout integrated circuit (ROIC) is proven. Integration of an OPD with a ROIC offers several benefits, including a larger fill factor and thinner sensor structure, it enhances the sensitivity of organic image sensor to achieve the wide dynamic range image.
 Large-are Processibility
Large-are ProcessibilitySolution processable OPD offers possibility of using spin or slot-ide coating to fabricate the device, compatible to large area process up to 12 inch wafer and Gen 8.5 TFT glass or plastic substrate with high throughput.
 Small CO2 Footprint and Environmental Friendly
Small CO2 Footprint and Environmental FriendlyOPD, being lead-free and contain no rare earth materials, can be fabricated by non-vacuum and low temperature process, using low energy consumption and produces less CO2 compares to that of the state of art semiconductor process.